The BEI, or Brand Equity Index, is an indicator that measures the perceived value of a brand by consumers. This index is particularly useful for comparing several brands with each other, or for evaluating a brand within a portfolio of brands.
The idea behind EIB is simple: the more a brand is known, considered and preferred by consumers, the higher its value. These are the three main elements involved in calculating the EIB.
EIB components
- Brand Awareness:
This is the percentage of consumers who are aware of the brand. For example, if 75% of people know about brand X, its awareness rate is 75. - Brand Consideration:
This percentage indicates how many consumers would consider buying the brand among those who know it. If 60% of people who know brand X think they might buy it, its consideration rate is 60. - Brand Preference:
This percentage represents how many consumers prefer this brand over its competitors. For example, if 50% of consumers prefer brand X to its competitors, then its preference rate is 50.
The EIB Formula
Now that we know the three components, let’s see how they combine in the EIB formula:
BEI = (Knowledge Rate * Consideration Rate * Preference Rate) / (100^2)
Explanation of the formula :
- We multiply the three rates (Knowledge, Consideration and Preference) together.
- Then, to make the result easier to interpret, we divide by 1002, i.e. 10,000, which normalizes the result to a more readable scale.
Practical example
Let’s take an example.
- Brand X is known by 75% of consumers (Knowledge Rate = 75).
- Among these consumers, 60% would consider buying this brand (Consideration Rate = 60).
- And finally, 50% of consumers prefer this brand to its competitors (Preference Rate = 50).
If we apply the formula, we get :
BEI = (75 × 60 × 50) / (100^2) = 225000 / 10000 = 22.5
Therefore, the brand equity index for brand X is 22.5.
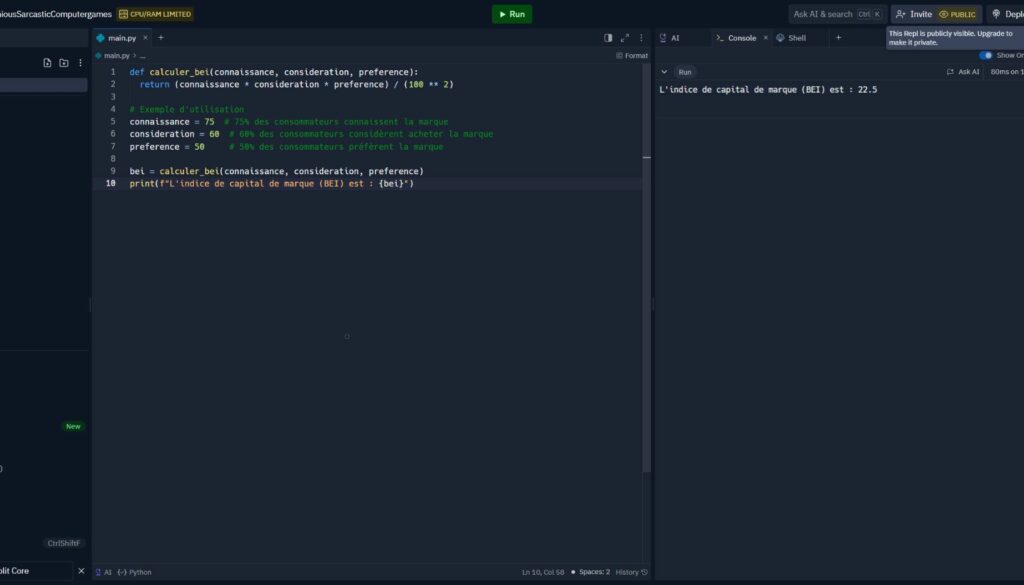
Python example
def calculer_bei(connaissance, consideration, preference):
return (connaissance * consideration * preference) / (100 ** 2)
# Exemple d'utilisation
connaissance = 75 # 75% des consommateurs connaissent la marque
consideration = 60 # 60% des consommateurs considèrent acheter la marque
preference = 50 # 50% des consommateurs préfèrent la marque
bei = calculer_bei(connaissance, consideration, preference)
print(f"L'indice de capital de marque (BEI) est : {bei}")- BEI helps you know how strong a brand is based on consumer awareness, consideration and preference.
- The higher the rates, the more important the BEI, which means that the brand is well perceived.
It’s a simple but powerful tool for assessing a brand’s perceived value in the marketplace!
Interpreting the EIB
Scale and context
The BEI (Brand Equity Index) is an indicator which, by its very nature, depends on the percentages of awareness, consideration and preference of a brand in relation to its competitors. The BEI is interpreted on a scale generally ranging from 0 to 100. A high BEI indicates a well-positioned brand in the minds of consumers, while a low BEI indicates a less successful or less recognized brand.
An EIB above 20 is often seen as positive, but this depends on the industry and competing brands. The EIB must always be analyzed in relation to the market, the sector, and the targeted consumer segments.
Limits and considerations
BEI relies on subjective data linked to consumer perception, which can make it sensitive to variations in surveys and purchasing behavior. Here are a few limitations to bear in mind:
- Survey data: BEI often relies on consumer surveys, and the quality of these data depends on sampling and response bias.
- Evolving over time: Brand perceptions evolve, and BEI can fluctuate rapidly according to trends, advertising campaigns or external events.
- Competition: EIB must always be interpreted in relation to competition. A brand may have a high EIB in a highly competitive market, but remain vulnerable.
Strategic implications
Marketing strategy
BEI is a key benchmark to guide marketing decisions. A high BEI indicates a strong brand, which may justify a strategy of maintaining or strengthening the current position through awareness campaigns, loyalty initiatives or reinforcement of competitive advantages.
On the other hand, a low BEI suggests a need to increase brand visibility or reposition the brand to improve consideration and preference. This could require actions such as discounts, promotions, or adjustments in marketing messages to better reach the consumer.
Product development
BEI can also guide the development of new products or services. A high BEI may signal a good time to launch spin-off products or brand extensions, as consumers have strong confidence in the brand. In the case of a low BEI, it may make more sense to strengthen brand identity before launching new products.
Brand management
Brand management must take BEI into account in order to maintain positive consumer perceptions and strengthen emotional bonds. If BEI reveals low brand preference, re-engagement efforts through repositioning campaigns or improving perceived values may be necessary.
Conclusion
Summary of key points
BEI is an important indicator of a brand’s strength in the marketplace. It is based on consumer awareness, consideration and preference. A high BEI means a strong, well-perceived brand, while a low BEI may indicate gaps in brand awareness or appeal.
The importance of BEI in marketing decisions
BEI enables marketers to better understand where to focus their efforts: strengthening a strong brand or revitalizing a weaker one. It influences strategic decisions such as product launches, optimization of communication campaigns and overall brand management. Proper use of BEI helps maximize a brand’s long-term value.